Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Aaron Blake
Have you ever wondered why your car sometimes feels twitchy or hard to control on the road? The secret often lies in something called steering geometry.
This is the hidden setup that directly affects how your vehicle responds when you turn the wheel. Understanding how steering geometry works can transform your driving experience, making your car feel smoother, safer, and more precise. Keep reading, and you’ll discover simple yet powerful insights that can help you take full control of your ride.
Credit: www.academia.edu
Contents
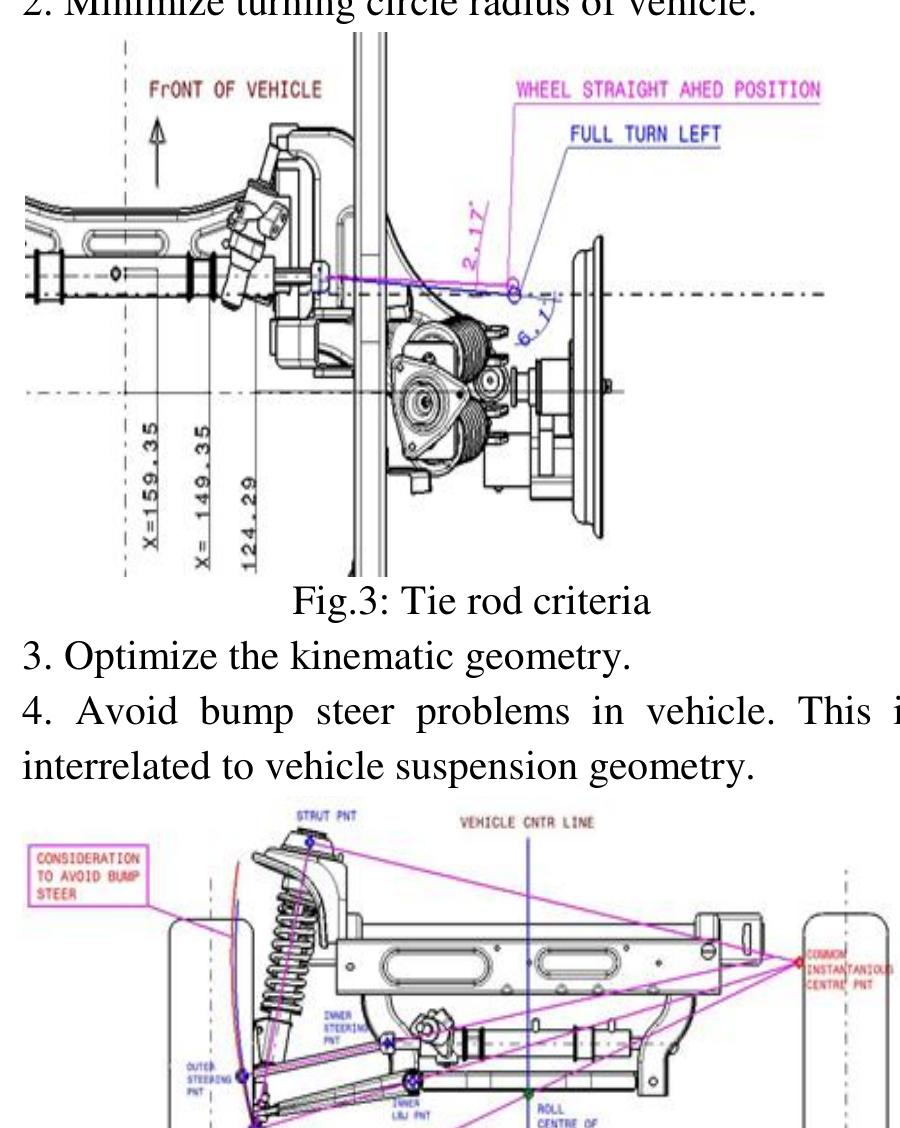
Key Components Of Steering Geometry
Steering geometry is the setup of parts that control how your car’s wheels turn. It affects how the car handles on the road.
Good steering geometry helps the car stay stable and respond well to your driving. It depends on several key parts.
Caster Angle
The caster angle is the tilt of the steering axis from the front to the back. It helps the wheels return to center after a turn.
A positive caster angle improves straight-line stability and steering feel. Too much can make steering hard.
Camber Angle
Camber angle is the tilt of the wheels from top to bottom. It affects how much the tires touch the road during turns.
Negative camber helps cornering grip by leaning the tire inward. Positive camber is rare and can reduce handling.
- Negative camber: top of the tire leans inward
- Positive camber: top of the tire leans outward
- Zero camber: tire is straight up and down
Toe Settings
Toe is the direction the tires point compared to the car’s centerline. It can be toe-in or toe-out.
Toe-in means the front of the tires point toward each other. It adds stability but can wear tires. Toe-out helps with quick turns.
| Toe Type | Effect on Handling | Tire Wear |
|---|---|---|
| Toe-in | Better straight-line stability | Increased wear on outer edges |
| Toe-out | Improved turn response | Increased wear on inner edges |
| Zero toe | Balanced handling | Even tire wear |

Credit: suspensionsecrets.co.uk
Impact On Vehicle Handling
Steering geometry shapes how a vehicle moves and reacts on the road. It affects safety and driving comfort.
Small changes in angles and alignment can change how a car handles corners and straight paths.
Cornering Stability
Proper steering geometry keeps the vehicle stable while turning. It controls how weight shifts during a corner.
- Correct camber angle improves tire grip in turns.
- Proper toe settings prevent the car from pulling sideways.
- Adjusting caster angle helps the wheels return to center smoothly.
Steering Response
Steering geometry affects how quickly the vehicle reacts to driver inputs. It can make steering feel light or heavy.
| Geometry Aspect | Effect on Steering |
|---|---|
| Caster Angle | Improves straight-line stability and steering feel |
| Toe Angle | Changes initial turn response and tire scrub |
| Camber Angle | Affects cornering grip and steering feedback |
Tire Wear
Steering geometry directly impacts how tires wear over time. Misalignment causes uneven wear patterns.
| Geometry Setting | Wear Pattern |
|---|---|
| Excessive Toe-in | Wear on outer edges |
| Excessive Toe-out | Wear on inner edges |
| Negative Camber | Inner edge wear |
| Positive Camber | Outer edge wear |
Adjusting Steering Geometry
Steering geometry changes how a car handles on the road. Proper adjustments improve control and safety. Incorrect settings can cause uneven tire wear and poor handling.
Adjusting steering geometry means setting angles and positions of the wheels. This keeps the car stable and responsive while driving.
Alignment Techniques
Wheel alignment sets the angles of the wheels to the car’s frame. It helps the car drive straight and reduces tire wear. Alignments include toe, camber, and caster angles.
Technicians use different methods to check and fix alignment. They measure angles and adjust parts to meet the car’s specs.
- Two-wheel alignment for front-wheel drive cars
- Four-wheel alignment for all-wheel drive cars
- Thrust angle alignment to center the rear wheels
Tools And Equipment
Special tools help measure and adjust steering geometry. These tools ensure precise settings for safe driving.
Common equipment includes alignment racks and measurement devices. These tools check wheel angles and positions accurately.
- Alignment rack with sensors or cameras
- Steering wheel lock to keep the wheel steady
- Turn plates to measure toe angle
- Camber gauge to check wheel tilt
- Wrenches and jacks for adjustments
Common Adjustments
Adjustments fix problems with handling and tire wear. They change wheel angles to improve driving performance.
Technicians often adjust toe, camber, and caster angles. Each angle affects how the car turns and grips the road.
- Toe:Changes the direction wheels point inward or outward
- Camber:Tilts wheels inward or outward from the top
- Caster:Controls the steering wheel’s angle for stability
- Steering axis inclination:Affects how wheels return to center
- Setback:Adjusts if one wheel is behind the other
Performance Benefits
Steering geometry plays a key role in how a vehicle handles. It affects many parts of driving.
Good steering geometry improves control, safety, and the overall driving feel.
Improved Precision
Proper steering geometry helps drivers steer exactly where they want. This precision makes driving easier and more accurate.
- Better wheel alignment reduces drifting
- Correct toe and camber angles improve tire contact
- Minimized steering play gives faster response
Enhanced Safety
Steering geometry affects vehicle stability. It helps keep the car steady in turns and during sudden moves.
| Steering Aspect | Safety Effect |
| Camber Angle | Improves tire grip on curves |
| Toe Setting | Reduces tire wear and keeps direction |
| Caster Angle | Helps wheels return to center |
Optimized Driving Experience
Good steering geometry makes driving more comfortable and less tiring. It balances effort and feedback well.
- Smoother turns with less effort
- Consistent feedback from the steering wheel
- Reduced vibration and noise inside the car

Credit: escapecollective.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Steering Geometry In Vehicles?
Steering geometry is the arrangement of parts that control wheel direction and angle.
How Does Steering Geometry Impact Vehicle Handling?
It affects how smoothly and safely a vehicle turns and responds to the driver.
Why Is Camber Important In Steering Geometry?
Camber controls tire contact with the road, affecting grip and cornering.
What Role Does Toe Angle Play In Steering?
Toe angle adjusts wheel alignment, influencing stability and tire wear.
Can Incorrect Steering Geometry Cause Tire Problems?
Yes, wrong settings lead to uneven tire wear and poor vehicle control.
Conclusion
Steering geometry shapes how your car handles turns and straights. Small changes can make a big difference in control and safety. Proper setup helps you drive smoothly and with confidence. Poor geometry can cause uneven tire wear and harder steering.
Understanding these basics keeps your vehicle balanced and responsive. Keep your steering tuned to enjoy safer, easier driving every time. It’s worth the effort for better road performance.





